The World Health Organization estimates that 1.28 billion people between the ages of 30-79 years old have hypertension, and 46% of those individuals do not know they have high blood pressure. Many people are unaware of their high blood pressure because there may be no noticeable symptoms of the disease.1
Blood pressure should be monitored for all adults and is a routine part of most encounters with medical providers. A diagnosis of hypertension is not usually based off a single reading, but from a trend of high blood pressure readings on multiple office visits2. Uncontrolled hypertension can lead to more serious complications such as heart disease, kidney disease, and stroke1. For adults over the age of 65, some clinical guidelines recommend a blood pressure goal of <130/80 mm Hg. 2
The American Heart Association classifies the stages of hypertension as follows:
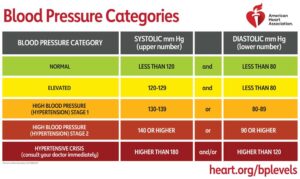
As seen in the American Heart Association “Understanding Blood Pressure Readings” American Heart Association. (n.d.). Understanding Blood Pressure Readings. www.heart.org. Retrieved March 21, 2023, from https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure/understanding-blood-pressure-readings
Lifestyle modifications are recommended to reduce blood pressure without the need for medications. Abstaining from smoking and reducing alcohol consumption are recommended in all adults for various reasons, and these choices can also help to lower blood pressure. Getting to a healthy body weight and increasing physical activity are also good strategies to manage high blood pressure. It is also recommended to reduce intake of foods with high sodium content because they can contribute to high blood pressure.2
If lifestyle modifications are insufficient to control hypertension, there are a few classes of medications that may be prescribed for people with hypertension. These drugs work by various pharmacological pathways and medication regimens are tailored to individual needs.4
Some examples of medications that may be used to control blood pressure are below:
| Thiazide diuretics | Calcium Channel Blockers (CCB’s) | Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
(ACE-inhibitors) |
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers
(ARB’s) |
Beta- Blockers |
|
|
|
|
|
References
- World Health Organization. (2023, March 16). Hypertension. World Health Organization. Retrieved March 21, 2023, from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension
- Benetos, A., Petrovic, M., & Strandberg, T. (2019). Hypertension management in older and frail older patients. Circulation Research, 124(7), 1045–1060. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.118.313236
- American Heart Association. (n.d.). Understanding Blood Pressure Readings. www.heart.org. Retrieved March 21, 2023, from https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure/understanding-blood-pressure-readings
- Whelton, P. K., Carey, R. M., Aronow, W. S., Casey, D. E., Collins, K. J., Dennison Himmelfarb, C., DePalma, S. M., Gidding, S., Jamerson, K. A., Jones, D. W., MacLaughlin, E. J., Muntner, P., Ovbiagele, B., Smith, S. C., Spencer, C. C., Stafford, R. S., Taler, S. J., Thomas, R. J., Williams, K. A., … Wright, J. T. (2017). 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/apha/ash/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension, 71(6). https://doi.org/10.1161/hyp.0000000000000065
